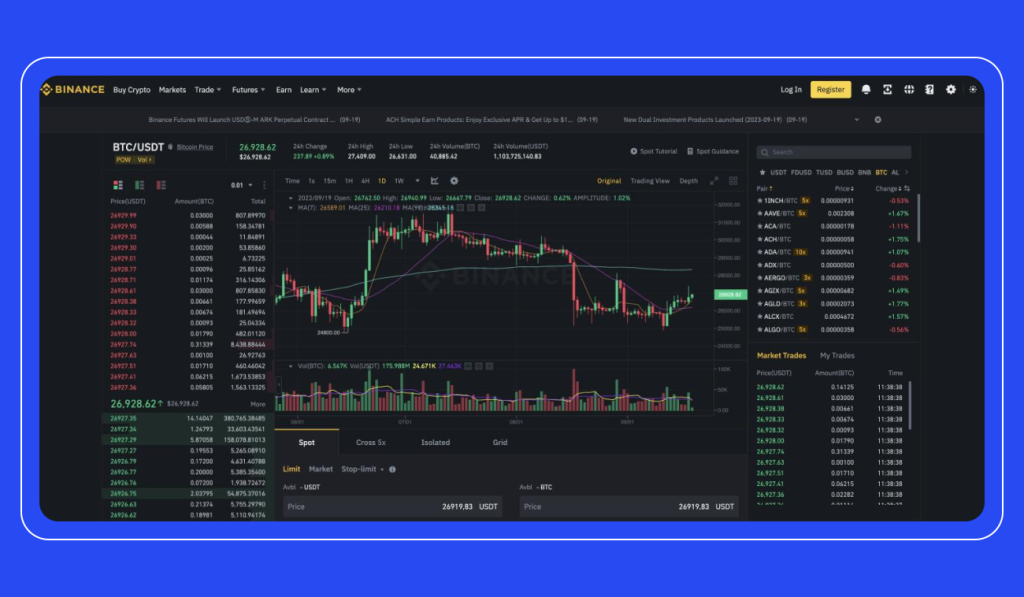
Binance is one of the world’s largest and most popular cryptocurrency exchanges, offering a comprehensive platform for trading a wide variety of digital assets. Understanding Binance trading involves grasping its core features, how users can engage in different types of trades, and practical use cases that demonstrate its functionality.
At its foundation, Binance provides spot trading where users buy and sell cryptocurrencies at current market prices. This straightforward method allows traders to exchange coins like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), or Binance Coin (BNB) directly with other market participants. The platform offers an intuitive interface with real-time charts, order books, and various order types such as limit orders, market orders, and stop-limit orders. These tools help traders execute precise strategies depending on their risk tolerance and investment goals.
Beyond spot trading, Binance supports futures trading which enables users to speculate on the price movements of cryptocurrencies without owning the underlying asset. Futures contracts allow leverage-borrowing funds to amplify potential gains or losses-which increases both opportunity and risk. For example, a trader anticipating that Bitcoin’s price will rise might open a long position using 10x leverage; if the price indeed rises by 5%, their profit could be magnified tenfold minus fees. Conversely, adverse price moves can lead to liquidation if margin requirements aren’t met.
Another key feature is margin trading where users borrow funds from Binance or other traders to increase their buying power in spot markets. This facility is useful for experienced traders who want larger exposure but must carefully manage risks due to interest costs and volatility.
Binance also offers decentralized finance (DeFi) integrations such as staking and liquidity pools directly on its basic platform mechanics. Staking allows holders of certain tokens to earn rewards by participating in network consensus mechanisms without active trading involvement. Liquidity provision incentivizes users to supply assets into pools used for decentralized exchanges (DEXs), earning fees proportionate to their contribution.
1. A retail investor may start by purchasing BTC through fiat gateways then diversify into altcoins using spot trades. 2. An active trader exploits technical analysis tools within Binance’s advanced charting suite coupled with futures contracts to capitalize on short-term trends. 3. Crypto enthusiasts stake BNB tokens via the Earn section generating passive income while holding onto assets. 4. Arbitrageurs monitor price discrepancies between Binance’s spot market versus other exchanges or futures markets aiming for low-risk profits. 5. Developers integrate API access provided by Binance enabling automated bots that execute predefined strategies round-the-clock.
In summary, understanding Binance trading requires familiarity with multiple product offerings including spot markets, leveraged futures contracts, margin loans, staking opportunities, and DeFi features embedded within the ecosystem. Practical application varies widely-from simple buy-and-hold tactics suited for beginners all the way up to complex algorithmic approaches favored by professional traders-making it a versatile platform catering broadly across user needs in today’s dynamic crypto landscape.



